Hospital stays can extend for reasons like complex medical conditions, post-operative complications, delays in organizing post-discharge care, and more. These extended stays can put significant pressure on healthcare systems, causing a strain on your existing resources and higher costs. For instance, resource bottlenecks, reduction in the availability of beds, and more.
To assess these stays and manage the challenges they bring along, hospitals often calculate the average length of stay (ALOS). ALOS is a simple metric that calculates the average number of days patients spend in the hospital between admission and discharge.
However, most healthcare institutions struggle to measure and analyze this metric accurately. They fail to capture reliable data that considers the complexity of patient care and hospital operations. They lose out on opportunities for identifying inefficiencies and resource misallocation thereby causing disruption in overall hospital performance. The primary reason for such situations is the absence of proper tools that offer real-time and actionable insights into ALOS.
In this article, we will explore the importance of measuring ALOS. We will also learn how to calculate it and introduce an intuitive ALOS calculator to assess patient stays and identify opportunities for improving hospital efficiency.
Importance of ALOS in Healthcare
Average Length of Stay measures the average duration that patients remain hospitalized in your healthcare facility during a single episode of care. It indicates the efficiency of a hospital and reflects how well healthcare facilities are managing their patient care. It helps gauge the efficiency of hospital operations and patient flow. It also assists in cost management by providing insights into resource utilization and potential areas for reducing unnecessary hospital stays.
According to the OECD, the average length of stay for acute care hospitalization in the U.S. was most recently found to be 6 days (2022 data). It has climbed every year since 2019, starting at 5.4 and continuing to the current average of 6.0. The ALOS values reflect the complexity of care and the hospital’s efficiency in managing patient stays.
A shorter ALOS is a strong indicator of:
-
- Better Patient Outcomes – Early discharge indicates that patients have been provided with the required medical attention and support. Additionally, it also reduces the chances of patients developing healthcare-associated conditions. For instance, infections, drug reactions, and other health-related issues. This ultimately results in improved outcomes for the patients.
- Decreased Costs – Reducing hospital stays leads to reduced expenses for both hospitals and patients. It lessens the hospital’s costs for treatment, staffing, medical supplies, bed occupancy, and other expenses.
- Strategic Planning – ALOS data is proven to be very beneficial for long-term planning purposes. It prepares you for upcoming healthcare demands. It can assist in predicting the demands for hospital resources, changes in patient numbers, possibilities for revenue growth, and more.
- Care Efficiency – A lower ALOS could also indicate streamlined operational processes. This means that patients receive quicker diagnosis and timely treatment at the right time without any unnecessary delays.
- Better Resource Allocation – A lower ALOS decreases the workload of physicians, nurses, and other hospital staff significantly and prevents burnout. You can free up your resources to handle emergency situations or surges in patient admissions. For example, beds, treatment equipment, medical supplies, and more.
While a longer ALOS indicates:
-
- Thorough Recovery – Patients with complex conditions may benefit from extended care as it enables comprehensive monitoring, rehabilitation, and treatment. It offers physicians more time to fine-tune their treatment plans and ensure patients leave the hospital in stable conditions.
- Increased Healthcare-Associated Risks – Extended stays can increase the risk of hospital-acquired infections, patient falls, or drug reactions. Patients staying too long in the hospital may also face psychological stress, impacting their overall recovery.
- Higher Operational Costs – Prolonged hospitalizations significantly increase costs for hospitals. You might have to hire additional staff, order extra medical supplies, and make space for new beds for patient occupancy.
- Resource Bottlenecks – Longer stays can impact bed availability and put a strain on existing hospital resources. It can also overburden healthcare workers. This leads to inefficiencies in hospital operations and causes delayed admissions for new patients.
- Reduced Readmission Rates – By ensuring patients are fully recovered before discharge, you can prevent premature releases. This results in lower readmission rates and improved overall patient outcomes.
Hence, hospitals should aim to eliminate avoidable delays by streamlining processes and ensuring timely treatments. This will ultimately lead to shorter and more efficient patient stays while maintaining high-quality care.
What is the Average Length of Stay Calculator?
The Average Length of Stay Calculator is a tool used by healthcare institutions to determine the average number of days patients stay in the hospital.
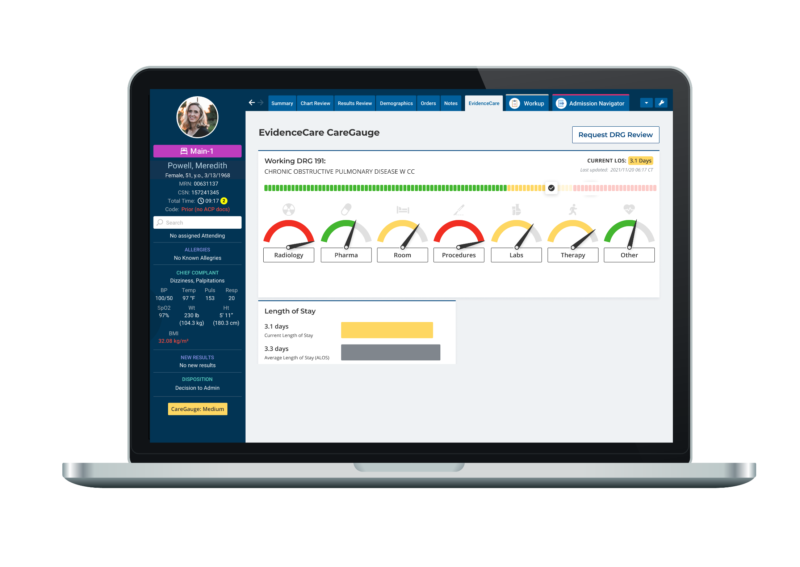
Software like CareGauge can help with tracking ALOS by using local benchmarked data based on specific DRG codes and CMS guidelines so doctors have targets to keep in mind for their patients.
An ALOS calculator can help you:
-
- track hospital performance by offering insights into its efficiency.
- identify areas of improvement for achieving better financial sustainability
How to Calculate Average Length of Stay?
ALOS is calculated by dividing the total number of days your patients have stayed in the hospital by the total number of patients discharged during a specific time period. This covers all patients regardless of how long they are hospitalized and how serious their conditions are.
The formula for calculating ALOS is as follows:
ALOS = Total number of inpatient days / Number of patient discharges
Let us consider the following example to understand how to calculate ALOS.
Suppose a hospital had 1000 patients who stayed in the hospital for a variety of treatments in August. And 250 people were discharged during the same month. Then, by applying the above-mentioned formula, we have:
ALOS = 1000 / 250 = 4 days
The average length of stay for August month is 4 days. This means the patients stayed in the hospital for 4 days on average before being discharged.
Remember,
-
- A high ALOS indicates that patients are staying in your hospital for longer durations. It could be for a variety of reasons, such as health complications, unavailability of post-discharge resources, inefficient care, and so on.
- Alternatively, a low ALOS suggests that your hospital is effectively discharging the patients. However, there is a chance of patients being discharged prematurely, which can lead to higher chances of readmissions.
Enhancing ALOS Calculations with AI and ML
The traditional method of calculating ALOS provides a basic overview of the length of stays. It fails to account for real-time data and patient acuity and delivers rough estimates regarding a patient’s health status, length of stay, and more.
Introducing AI and ML into your average length of stay calculator facilitates real-time data analysis and resource allocation at a granular level and offers more personalized predictions. It helps you make accurate LOS predictions to enhance the operational efficiency of the hospital.
For instance, you can plan for staff schedules, medical supplies, bed availability, and more in advance using various ALOS insights. You can also use these insights to avoid bottlenecks in high-demand units and prevent overcrowding by patients.
Moreover, AI and ML engines can identify patterns in patient data based on real-time changes. For example, new diagnoses, treatment plans, responses to new treatment procedures, and so on. This can help you identify risks early on and plan a personalized approach for delivering necessary care to the patient. Thus reducing premature discharges and frequent readmissions.
Integrating AI and ML with the ALOS calculator can turn the basic ALOS metric into a dynamic tool for better operational efficiency and impressive quality of care.
Reduce LOS with CareGauge
Reducing ALOS has become a top priority for hospitals to improve their efficiency and patient outcomes. Utilizing the power of automation and real-time data in your average length of stay calculator can help you streamline patient care, boost hospital performance, and minimize patient care delays. Thus making healthcare delivery efficient and cost-effective.
CareGauge is one such tool that leverages cutting-edge technology to reduce ALOS through real-time insights and data-driven recommendations. It offers a highly personalized view of patient information and care utilization insights so that you can deliver the right care at the hospital. You can compare your patients’ care journeys with benchmarked ones to reduce unnecessary treatment delays and improve care delivery.
It utilizes an algorithmic approach to ensure the right care is delivered at the right time, reducing unwarranted variation and prolonged LOS. This is further strengthened by the predictive length of stay based on DRG’s that can help you overcome these challenges proactively. In fact, CareGauge has proven to reduce the length of stay by 5+ hours per patient with its advanced functionalities.
Schedule a demo of CareGauge today to see how it can reduce your ALOS and optimize the hospital’s performance.