Unwarranted Variation in Healthcare
Variation in healthcare brings inconsistent or unjustifiable differences in clinical practice, health outcomes, and healthcare costs across providers or geographic regions. Unwarranted clinical variation exists when care that should be clinically equivalent varies in a way that cannot be explained by patient preferences or condition differences.
Additional problems associated with unwarranted variation in healthcare include wasted resources, increased costs, and compromised quality and safety. Recognizing and addressing unwarranted variation is crucial to improving healthcare value.
Some key types of clinical variation in healthcare include:
-
- Geographic variation: Differences in practice patterns, costs, and outcomes across geographic regions. For example, the frequency of surgeries for back pain varies significantly between states.
- Institutional variation: Differences between hospitals and health systems in the management, treatment options selected, and outcomes achieved for the same basic conditions.
- Physician practice variation: Differences in practice styles, technologies employed, and referrals to specialists. It also includes variations in hospital admission rates and utilization of procedures among physicians treating the same patient populations.
The practical use of variation related to health statistics allows the pinpointing of unwarranted variation and inefficient or overuse of medical practices. Variation analysis provides meaningful benchmarks, promotes transparency, and enables best practice sharing and course corrections.
Reducing variation in healthcare can achieve major benefits including:
-
- Improved quality and value: By standardizing necessary care and avoiding unnecessary care.
- Cost containment: By reducing overtreatment, inappropriate care, and wasteful spending.
- Equity of access: By providing consistent, evidence-based care regardless of demographics, geography, or payer.
- Better outcomes: By optimizing treatment based on data and guidelines rather than physician preference or local tradition.
So, what is variation in healthcare? In a nutshell, it refers to differences in healthcare practices, costs, test usage, treatments, outcomes, and procedures that cannot be explained by patient characteristics or condition differences. Addressing unwarranted variation in healthcare is key to improving affordability, safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, equity, and timeliness. By promoting standardized yet flexible best practices, U.S. healthcare can move closer to maximizing value and minimizing waste.
Unwarranted Variation Meaning
Unwarranted variation is a term used to describe the differences in healthcare delivery and outcomes that cannot be explained by the underlying clinical factors, such as patient demographics, disease severity, or medical history.
It’s important to distinguish between warranted vs unwarranted variation. Warranted variation refers to the differences in healthcare that are expected and justifiable. Unwarranted variation, on the other hand, is the variation that is deemed unnecessary, unjustifiable, or even unfair.
There are different types of variation in healthcare, including common cause variation in healthcare, which is the natural variation that occurs in any process, and special cause variation, which is the result of a specific factor or event. Unwarranted variation falls under the category of special cause variation, as it is not a natural or expected variation in healthcare delivery.
Clinical variation is another term used to describe the differences in healthcare delivery and outcomes. Clinical variation definition can include variations in the use of medications, tests, or procedures for the same medical condition. Some clinical variation examples include prescribing the same drug at different doses or frequencies for the same condition and ordering different tests for the same diagnosis.
Unwarranted variations in healthcare can lead to disparities in healthcare access, utilization, and quality. It is therefore essential to understand what unwarranted variation is and address it to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
While some level of acceptable variation in healthcare is expected and justifiable, unwarranted variation must be addressed through evidence-based guidelines. This will reduce financial incentives for unnecessary procedures, improve patient education and engagement, and implement policies to minimize avoidable variation.
Unwarranted Variation Examples
Unwarranted variation causes major differences in medical treatment and care among patients with similar conditions. Here are some unwarranted variations in healthcare examples:
-
- Geographic variation: Studies have shown that patients with the same condition may receive different treatments depending on where they live. For example, patients in some regions may be more likely to receive surgery for back pain. Others may receive physical therapy or medication, which are examples of variation in healthcare. This variation may be due to differences in physician training, local practice patterns, or availability of medical resources.
- Racial and ethnic variation: Research shows that racial and ethnic minorities frequently receive poor quality healthcare compared to non-minorities. This happens even when accounting for influences such as income and insurance coverage. This type of disparity could stem from biases among healthcare providers, language obstacles, or cultural differences in health views and customs.
- Gender variation: One clinical variation example is that women may receive different treatments compared to men for the same conditions, such as heart disease. This may be due to differences in symptom presentation, but it may also reflect biases among healthcare providers who may underestimate women’s risk for certain conditions.
Unwarranted variation can lead to differences in healthcare utilization and resource allocation. To address unwarranted variations in healthcare, organizations can implement quality improvement initiatives that aim to standardize care and reduce variability.
Reduce Unwarranted Variation in Healthcare
Now that we understand how warranted variation in healthcare is important, how can doctors contribute to decreasing variation in their professional practice? Well, to do this, doctors must first understand ways to reduce unwarranted care variation, such as standardizing protocols and procedures and comparing outcomes data. By sharing evidence-based best practices across units and facilities, hospital administrators can also decrease variation in healthcare in terms of the quality and efficiency of patient care.
Hospitals and doctors must also work to reduce unwarranted clinical variation and ensure patients receive the warranted standard of care. Some key strategies on how hospitals can reduce variation include:
-
- Developing evidence-based clinical guidelines and protocols to guide decision-making. Following guidelines helps avoid unnecessary variation in diagnosis and treatment.
- Measuring and transparently reporting outcomes, costs, patient experiences, and other key metrics to identify areas of unwarranted clinical variation. Looking for opportunities to normalize best practices.
- Investing in quality improvement, initiatives focused on reducing waste, streamlining care processes, and optimizing resource utilization. This decreases variation in the costs and intensities of care.
- Providing data and decision support tools to help providers make more standardized care choices. Tools like predictive modeling can suggest the most effective, low-variation approaches.
- Educating all staff on the importance of reducing unwarranted variation and ensuring a shared understanding of key goals. A culture focused on value, quality, and efficiency will naturally decrease unnecessary variation.
- Fostering collaboration through communities of practice, mentoring, and partnership across organizations. Coordinated, multi-site efforts are most effective at achieving meaningful reductions in healthcare’s warranted variation.
Reducing variation, meaning lessening the likelihood that patient treatment for the same diagnosis differs significantly, is essential to ensure that every patient receives the right care every time. It’s key to improving quality, controlling costs, and achieving the triple aim of better health, better care, and lower costs. By standardizing best practices and measuring/optimizing outcomes, the healthcare system can decrease care variation and realize its promise of value-based care.
Healthcare Variation Reduction Software
Unwarranted variations in costs, quality, and outcomes plague the U.S. healthcare system. Even for the same procedures or conditions, costs can vary significantly between different hospitals and healthcare providers. This leads to higher spending, inconsistencies in care quality, and unpredictable patient experiences.
Healthcare variation reduction software is an application designed to help healthcare professionals reduce variation in clinical processes, treatments, and outcomes. The software uses comparative data analytics, machine learning, and other advanced technologies to identify patterns and trends in healthcare data and provide insights into the factors contributing to variations in patient care.
Care variation software helps healthcare organizations gain insights into these variations and take action to optimize costs, standardize quality, and improve outcomes. EHR healthcare variation software works by analyzing cost data, utilization data, claims data, electronic health records (EHR), and other metrics across all areas of a healthcare system. The solutions uncover unwarranted variances and opportunities for improvement. The EMR healthcare variation software then provides recommendations and tools to help reduce or eliminate unnecessary variations meaningfully and sustainably.
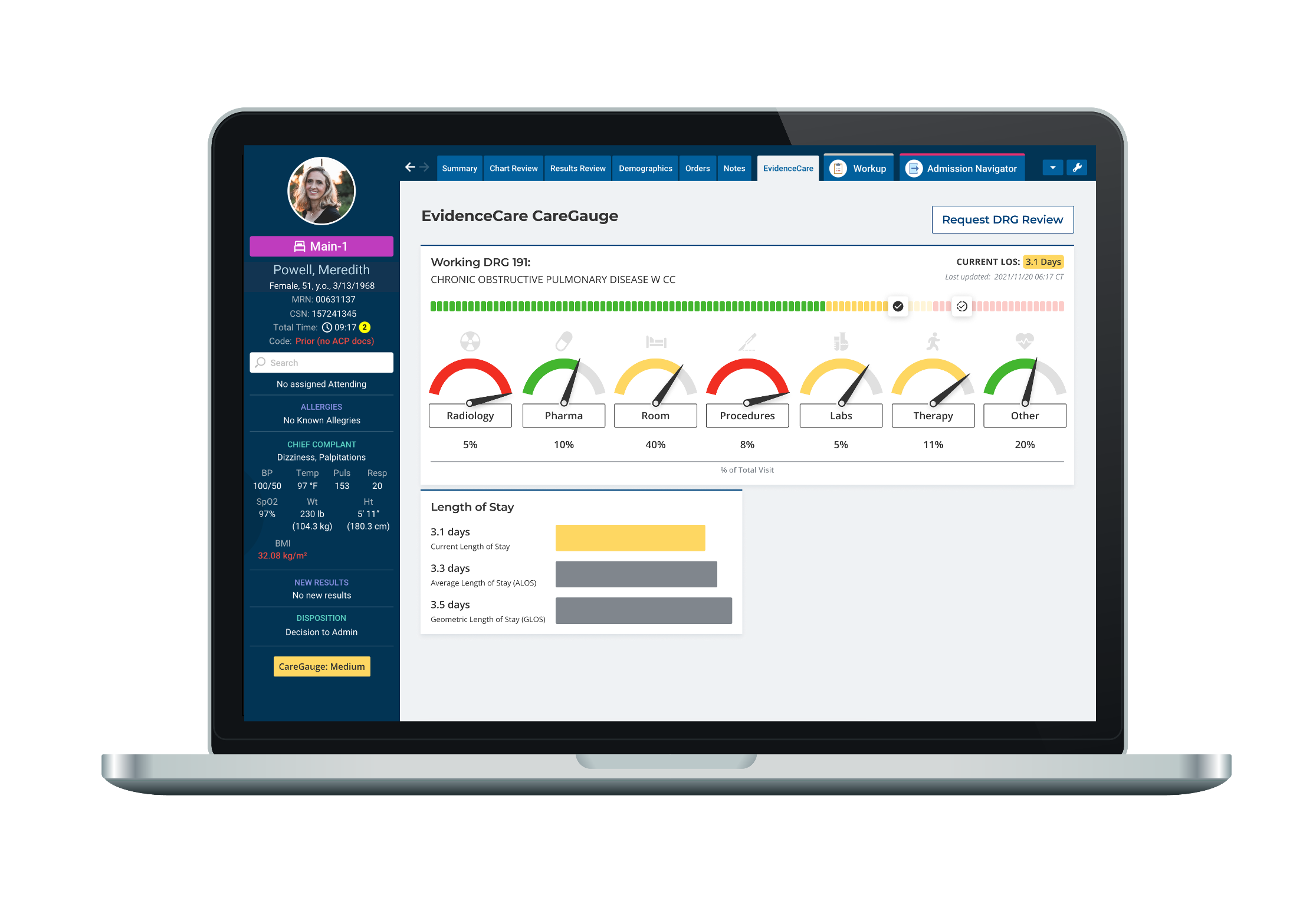
Of the various clinical variation software available today, CareGauge by EvidenceCare stands out as the leading option. Some of the key benefits of using CareGauge include:
-
- Deep analytics and insights: CareGauge analyzes massive amounts of hospital-specific and peer-compared data to uncover variations in costs, quality, utilization, and more.
- Personalized, data-driven recommendations: CareGauge provides customized recommendations and insight for each patient and diagnosis-related group (DRG) based on their specific opportunities for improvement.
- Easy optimization: CareGauge integrates into EHR systems such as Epic, Cerner, and MEDITECH to facilitate the implementation of real-time recommendations and help reshape practices in a simple, streamlined way.
- Measurable savings: On average, CareGauge hospitals achieve $325 of savings per discharge or more through reduced unwarranted variation.
- Improved outcomes: By standardizing high-value best practices, CareGauge helps ensure all patients receive the most effective, evidence-based care possible, leading to better outcomes, experiences, and quality metrics.
By partnering with EvidenceCare, healthcare organizations can optimize costs, enhance quality, improve outcomes, and move closer to achieving the triple aim. CareGauge is the clear choice for any organization looking to reduce unwarranted variation and ensure sustainable success.
Interested in learning how CareGauge could make a difference at your hospital? Schedule a demo today.