Two Midnight Rule
The Two-Midnight Rule is a policy implemented by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to help differentiate whether a patient’s hospital stay should be considered inpatient or outpatient care. This rule has had a significant impact on hospital billing practices and Medicare reimbursements and consequently has found itself at the forefront of many discussions in the medical industry. It’s very important for both healthcare providers and patients to understand the Two-Midnight rule and how it can affect medical costs in 2023 and beyond.
What Is the Two-Midnight Rule?
Established by CMS in 2013, the Two-Midnight rule dictates that if a physician expects a patient to require hospital care that spans at least two midnights, the patient should be classified as an inpatient. If the anticipated duration of stay is less than two midnights, the patient is considered an outpatient under observation status. The CMS Two-Midnight Rule was originally designed to address concerns about hospitals keeping outpatients under observation for extended periods of time when their services should actually be considered inpatient stays.
The Two-Midnight Rule Explained
The classification of inpatient vs. outpatient has a major influence on Medicare reimbursements since inpatient stays are covered by Medicare Part A while outpatient services are covered by Medicare Part B. Inpatient stays covered under Part A usually include a deductible but limit out-of-pocket expenses incurred during admission. On the other hand, outpatient services covered by Part B often involve copayments that are capped at the inpatient deductible amount.
Two-Midnight Rule Compliance
It’s crucial to grasp the nuances of the CMS Two-Midnight Rule when navigating medical billing systems or addressing insurance coverage concerns. Healthcare providers must always remain compliant with this rule to avoid audit risks and potential financial penalties.
CMS Two-Midnight Rule (2023)
The Two-Midnight Rule helps guide hospitals and physicians on appropriate admission statuses for patients. It also plays a pivotal role in determining Medicare reimbursement rates and helping beneficiaries understand their medical bills. As the healthcare sector progresses, it’s vital for all involved parties to remain informed about the nuances of the Two-Midnight Rule. With this knowledge in hand, healthcare providers can continue delivering quality care, mitigating potential billing disputes, and fostering transparent relationships with their patients.
Criteria of the Two-Midnight Rule
The criteria for the Two-Midnight Rule have been the subject of much discussion and analysis among healthcare professionals since its introduction in 2013. The Two-Midnight rule was established to provide clearer guidelines for determining whether a patient should be classified as an inpatient or remain under observation status as an outpatient during their hospital stay. Understanding these criteria is crucial for both hospitals and patients, as it affects reimbursement rates and financial responsibilities significantly.
Two-Midnight Rule for Inpatient Admissions
So, what are the criteria for being admitted as an inpatient under the two-midnight rule? One key component of the Two-Midnight Rule is to define “two-midnight rule observation stays.” Essentially, this means that if a physician believes a patient will require care that spans at least two midnights, they should be admitted as an inpatient. Conversely, if the necessary care can be reasonably completed before two midnights have passed, the patient is generally considered to be under observation status. Though there can be exceptions to this rule. It’s important to note that observation stays are classified as outpatient services, which can result in higher out-of-pocket costs for patients.
To make it easier to navigate the Two-Midnight Rule, healthcare providers could consider using a Two-Midnight Rule flowchart to guide them in making appropriate admission decisions. An effective flowchart might account for factors such as:
-
- The severity of symptoms
- The patient’s medical history
- Related risk factors
- Whether any required procedures are included on the CMS Two-Midnight Rule “inpatient only” list
How does the Two-Midnight Rule apply to Medicare Advantage plans?
According to the recent CMS final rule for CY 2024, Medicare Advantage (MA) plans must follow the two-midnight rule in 2024. They must provide coverage when an admission is based on complex medical factors that are documented in the chart, and the admitting clinician feels that the care will require at least two midnights.
Medicare Advantage plans follow similar CMS guidelines concerning hospital admissions and reimbursements. However, individual insurers may have specific requirements or definitions regarding what constitutes inpatient versus outpatient care. As such, providers must consult with each insurer directly for any clarifications needed about policy adherence.
Compliance with the Two-Midnight Rule is essential for any hospital seeking proper reimbursement from Medicare and other insurance companies. Compliance is also crucial for avoiding potential penalties associated with improper admissions. To remain compliant, hospitals must meet the CMS’s 2-midnight rule documentation requirements, which involve thorough and accurate record-keeping of each patient’s medical necessity for inpatient admission, including the physician’s expectations and rationale for their decision.
It’s vital for healthcare providers to understand the criteria of the Two-Midnight Rule in order to make informed decisions about hospital admissions and ensure compliance with CMS guidelines. By adhering to these criteria, hospitals can optimize their reimbursements, minimize potential penalties, and, most importantly, deliver appropriate care to their patients.
Two-Midnight Rule Challenges
The Two-Midnight rule is a critical component of the decision-making process for hospitals and healthcare providers when determining appropriate billing statuses for patients. Introduced by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), this rule stipulates that inpatient admissions are only considered reasonable and necessary if the physician believes that a patient’s treatment will span at least two midnights.
What are the exceptions to the Two-Midnight Rule?
However, there are a few challenges and exceptions associated with the Two-Midnight Rule. One of the most common Two-Midnight Rule exceptions is when CMS recognizes ‘rare and unusual’ circumstances. In such cases, an acute medical condition may require hospitalization even if it does not satisfy the two-midnight benchmark. For instance, procedures or surgeries typically completed within 24 hours might warrant inpatient admission based on the patient’s unique situation or physician’s judgment. These instances must be thoroughly documented to justify deviation from standard guidelines.
Another notable Two-Midnight Rule exception applies to patients under Medicare Advantage plans, which operate differently than traditional Medicare policies. The implications of the Two-Midnight Rule for Medicare Advantage plans vary because private insurance companies administer these plans rather than government agencies. Consequently, the specific criteria and billing requirements for inpatient admissions may differ from those established under traditional Medicare regulations. Healthcare providers need to understand each plan’s policies to ensure compliance with their respective rules.
How has the Two-Midnight Rule impacted the design and operations of healthcare?
Despite its intentioned benefits, the Two-Midnight Rule has also introduced some challenges and prompted extensive debate among stakeholders within the healthcare industry. Some physicians argue that this regulation undermines their clinical expertise by imposing arbitrary time constraints on medical decision-making processes.
Additionally, certain facilities face increased financial pressures due to shifting patient populations away from inpatient admissions and towards outpatient services or observation stays. Some hospitals have had to adapt their infrastructure and staffing models to accommodate these changes.
There are also concerns about the potential overuse of observation stays because they fall outside of Two-Midnight Rule parameters — despite being potentially indistinguishable from inpatient care in practice. This ambiguity forces hospitals into a precarious balancing act between ensuring optimal patient care and avoiding potential noncompliance penalties.
The Two Midnight Rule has impacted the design and operations of healthcare facilities in significant ways. Providers must remain vigilant in navigating challenges and exceptions to ensure compliance and maintain their commitment to delivering high-quality patient care. In coming years, continued dialogue among industry stakeholders will be crucial to help refine policy guidelines in ways that account for both necessary regulatory requirements and the realities of clinical practice.
Future of the Two-Midnight Rule
The future of the Two-Midnight Rule is a topic of debate in the healthcare industry. As healthcare policies evolve and the industry becomes more and more dependent on software, it becomes ever more critical to consider the role this rule might play in the coming years.
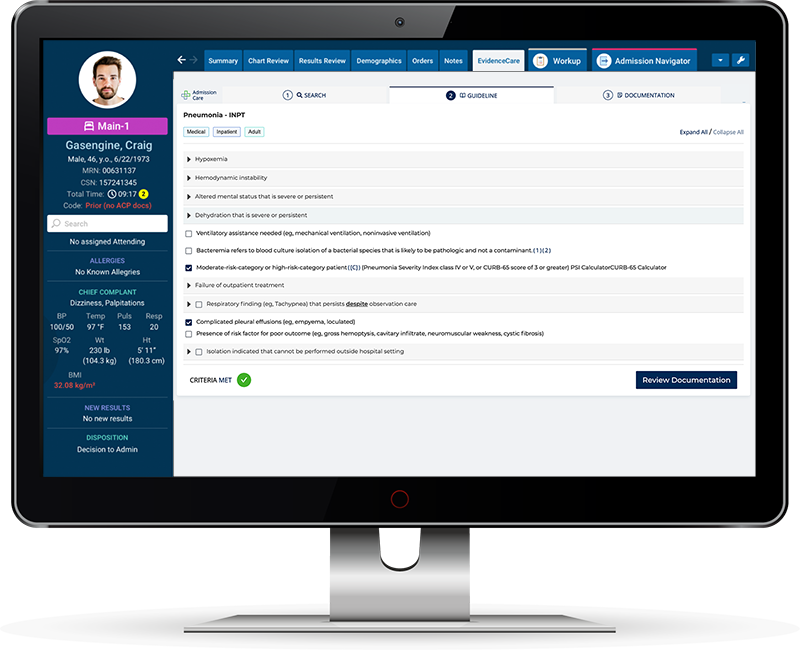
One key aspect of the evolution of the Two-Midnight Rule is the development of Two-Midnight Rule software, such as EvidenceCare’s AdmissionCare. Implementing this kind of technology can help hospitals accurately determine whether a patient meets the criteria for hospital admission under the Two Midnight Rule as well as streamline billing processes.
AdmissionCare software for hospital admissions can significantly improve efficiency within medical facilities by reducing administrative workloads and assisting with crucial decision-making tasks.
This area of rapid advancement is also known as admission criteria software. Access to reliable and up-to-date information on patient eligibility is more critical than ever for hospitals. Admission criteria software programs can assist physicians in making informed decisions when it comes to admitting patients and ensuring compliance with CMS guidelines — like MCG and Interqual – including guidelines related to the Two-Midnight Rule. Resources like a 2-midnight rule guide can be invaluable for anyone seeking more information on this topic.
As we look toward future improvements to the CMS 2 Midnight Rule, it’s crucial to account for real-life examples of the rule’s application. Analyzing Two-Midnight Rule examples can provide opportunities to identify areas where further clarity or updates may be needed.
Evolving medical documentation guidelines and technological innovations will inevitably impact how healthcare providers navigate the Two-Midnight rule in years to come. By staying informed about the latest advancements and understanding the implications for patient care, hospitals can ensure they’re not only following regulations but also providing the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Want to ensure compliance and medical necessity documentation for all your hospital admissions?
Schedule a demo of AdmissionCare today.