Inpatient Vs. Observation Criteria
Understanding the distinction between inpatient vs. observation criteria is crucial for patients and healthcare providers regarding hospital admissions. Inpatient status refers to formal admission to the hospital, where the patient receives comprehensive medical care and typically stays over two midnights.
On the other hand, observation status indicates that a patient is closely monitored to determine if further treatment as an inpatient admission is necessary or if they can be discharged. The decision between these two statuses, inpatient vs. observation, depends on specific criteria and well-documented clinical judgement to ensure appropriate medical care and reimbursement.
The criteria for determining inpatient vs. observation criteria can vary based on several factors, including the patient’s medical condition, the severity of symptoms, required interventions, and anticipated length of stay.
Typically, inpatient admission criteria are met when a patient’s condition requires ongoing medical management and treatment, necessitating a more extended hospital stay. In contrast, observation admission criteria are assigned when a patient’s condition is uncertain or requires additional evaluation, diagnostic tests, or short-term monitoring before making a definitive decision.
The time a patient can spend as an inpatient vs. how long a patient can be in observation status also plays a role in the decision-making process. Inpatient stays are typically more extended, lasting several days or more, depending on the severity and complexity of the patient’s condition.
On the other hand, observation stays are usually shorter, lasting less than 48 hours. However, it is essential to note that these timeframes can vary based on the specific circumstances and the guidelines set forth by the hospital and regulatory bodies.
Hospitals follow specific inpatient admission criteria and guidelines, including those outlined by Medicare, to ensure compliance and appropriate reimbursement. Medicare sets particular criteria for inpatient admission, emphasizing the medical necessity and severity of the patient’s condition. For observation status, Medicare provides guidelines that focus on the need for:
-
- short-term assessment
- monitoring, or additional diagnostic tests
Why do Hospitals use observation status?
Hospitals utilize observation status for several reasons. First, observation allows medical professionals to assess patients’ conditions over a shorter period, usually less than 48 hours, to determine if further treatment or admission is necessary.
This approach enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding patient care without immediately committing to inpatient admission.
Moreover, observation status is often used when the severity of the patient’s condition is uncertain, or the treatment plan requires additional diagnostic tests or monitoring. This status allows for a thorough evaluation before deciding on the appropriate level of care.
Additionally, observation status can help mitigate the risk of inappropriate admissions, ensuring that hospital resources are allocated effectively and efficiently. By utilizing observation care, hospitals can optimize bed availability for patients requiring more intensive treatments or procedures.
It is important to note that observation status is subject to specific guidelines, including those outlined by Medicare. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) provides guidelines for observation status, which include Medicare observation hours limiting the number of observation hours allowed before a decision is made regarding the patient’s status.
The Medicare Two-Midnight Rule is an essential aspect of these guidelines, stating that inpatient admission is generally appropriate when the physician expects the patient’s stay to span at least two midnights.
Understanding why hospitals use observation status is valuable for patients and healthcare providers. Patients can be reassured that their conditions are being thoroughly assessed and that the appropriate level of care will be provided based on their specific needs. It also can have huge financial implications for the patient and hospital. Healthcare providers can use observation status to:
-
- ensure accurate diagnoses
- minimize inappropriate admissions
- and optimize resource utilization within the hospital
How to avoid observation status or change from observation to inpatient status?
Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate the patient’s
-
- condition
- medical necessity
- and expected length of stay
It is essential to adhere to CMS guidelines for observation status and ensure that the patient’s care plan aligns with the necessary criteria for inpatient admission.
Types of Hospital admission criteria
Hospitals rely on various types of hospital admission criteria to determine whether a patient should be classified as an inpatient or placed under observation status. Three commonly used sets of guidelines are the Milliman Care Guidelines (MCG), InterQual, and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) guidelines for criteria for hospital admission.
-
- MCG criteria provide evidence-based guidelines for assessing medical necessity, focusing on factors such as the severity of the patient’s condition, the complexity of care required, and the expected length of stay. These guidelines help healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding the appropriate level of care.
- InterQual criteria guidelines also play a significant role in guiding hospital admissions. They consider medical necessity, the severity of illness, service intensity, and care appropriateness. InterQual criteria help determine whether a patient’s condition meets the requirements for inpatient care.
- The CMS criteria for hospital admission are specific to Medicare and Medicaid patients. They outline particular criteria that must be met for hospital admission to be considered medically necessary and qualify for reimbursement. CMS guidelines for observation status emphasize factors such as the severity of the patient’s symptoms, the need for diagnostic procedures, and the potential risks of delaying treatment.
By following these admission criteria, hospitals can ensure that patients receive the appropriate level of care based on their medical needs.
These guidelines help healthcare professionals make objective and informed decisions regarding inpatient or observation status. They also play a crucial role in determining the eligibility for reimbursement under specific insurance programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid.
Understanding and implementing these guidelines are essential for hospitals to provide high-quality care, optimize resource utilization, and ensure compliance with reimbursement regulations. By using the MCG criteria, InterQual criteria, and CMS guidelines for observation status, healthcare providers can assess the medical necessity and severity of patients’ conditions accurately, resulting in appropriate and efficient hospital admissions.
CMS Observation Guidelines 2023
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services periodically update their observation and CMS inpatient billing guidelines to ensure compliance with evolving healthcare practices. The CMS observation guidelines 2023 provide specific criteria that hospitals must consider when determining observation status.
These CMS guidelines for inpatient admission 2023 emphasize the importance of medical necessity and require hospitals to comprehensively assess the patient’s condition. They outline specific factors such as:
-
- the presence of unstable or unpredictable symptoms
- the need for short-term intensive monitoring or assessment
- and the requirement for diagnostic tests or procedures
Hospitals can ensure appropriate patient classification and reimbursement by adhering to the CMS observation guidelines 2023.
Adhering to the CMS observation guidelines 2023 is crucial for hospitals as it ensures proper patient classification and reimbursement. The guidelines help hospitals decide whether patients should be placed under observation status or require inpatient admission. By accurately assessing the patient’s condition and applying the CMS criteria, healthcare providers can effectively determine the most appropriate level of care for everyone.
The CMS observation guidelines 2023 reflect the CMS’s commitment to maintaining high standards of care and reimbursement practices. They provide healthcare professionals with a framework for evaluating patients’ needs and ensuring that observation status is utilized when necessary. Hospitals can meet compliance requirements and ensure appropriate billing practices by following these guidelines.
Staying up to date with the CMS observation guidelines 2023 is essential for hospitals to navigate the complexities of patient classification and reimbursement. By understanding and implementing these guidelines, healthcare providers can provide optimal care, manage resources effectively, and maintain compliance with CMS regulations.
Inpatient vs. Observation Software
Traditionally, utilization review (UR) teams in hospitals are responsible for ensuring admission criteria and guidelines are appropriate, while doctors focused on patient care. Most doctors aren’t aware of the nuances of admission criteria, which leaves the UR team with a lot of “clean-up” work on the back-end.
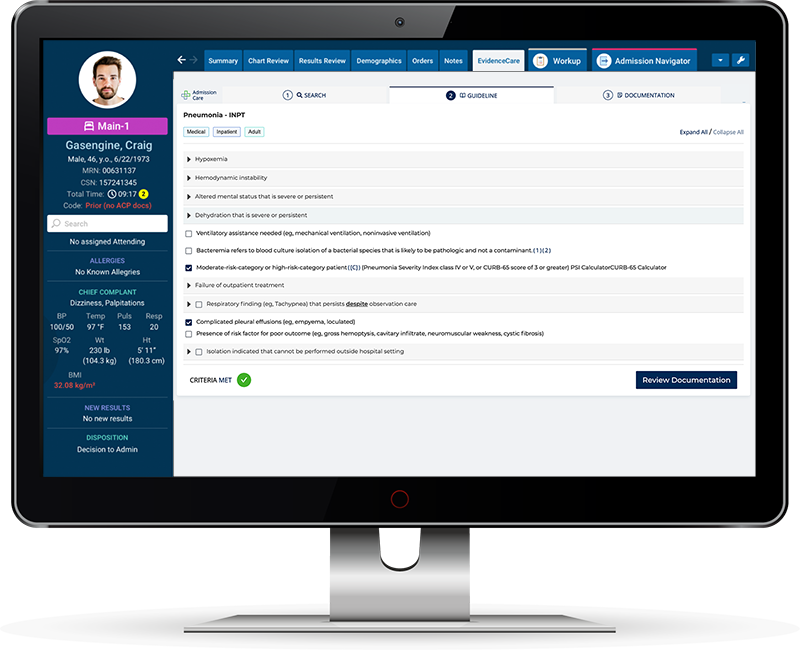
However, EvidenceCare’s software, AdmissionCare, revolutionizes this process by providing admitting physicians and hospitalists with the automated medical necessity documentation directly in the EHR to accurately choose between inpatient vs. observation criteria.
AdmissionCare saves hospitals time and money by equipping physicians with the appropriate bed status and medical necessity documentation at the time of admission. By eliminating the need for UR teams to approach physicians and hospitalists for documentation, this software:
-
- streamlines the hand-off process
- reduces denials and secondary level reviews
- and minimizes administrative burdens.
The software incorporates the established guidelines, such as MCG criteria, InterQual criteria, and CMS criteria for hospital admission, into its framework. It ensures that physicians can access the most up-to-date criteria and make informed decisions regarding patient status. By using AdmissionCare, hospitals can enhance efficiency, increase revenue, improve compliance with admission guidelines, and optimize resource allocation.
Physicians empowered with the right criteria can make accurate determinations between inpatient vs. observation criteria, facilitating appropriate patient care while aligning with reimbursement requirements.
In conclusion, understanding the distinction between observation status vs. inpatient admission – guidance for physicians – is crucial for hospitals to provide appropriate care and ensure proper reimbursement. Guidelines such as MCG, InterQual, and CMS play a significant role in determining patients’ appropriate level of care.
Additionally, the implementation of software like AdmissionCare empowers admitting physicians with the necessary criteria and documentation, streamlining the process and reducing administrative burdens.
By following these guidelines and leveraging innovative software solutions, hospitals can optimize patient care, improve efficiency, and enhance healthcare delivery.
Schedule a customized demo here if you’d like to see what it’d be like to use AdmissionCare with your EHR.